Scaling AI Agents Across Industries—and Navigating the Risks

Principal Engineer

The impact of AI is already discernible across industries. Let’s be blunt: AI agents aren’t just coming—they’re gutting inefficiencies right now. When a $12B logistics giant slashes delivery times by 40% overnight using route-optimizing agents, that’s not “innovation.” It’s extinction-level disruption for competitors still pushing spreadsheets. AI-driven route optimization leads to real, on-the-ground improvements.
Across sectors, a major legal firm’s AI system can review commercial contracts in seconds, a task that once consumed thousands of hours annually for paralegal teams. These are not incremental gains; they signify profound shifts in operational efficacy and resource utilization.
The potential applications of AI agents across various sectors are only expanding:
- Manufacturing & Logistics: Agents can manage inventory, predict machinery maintenance needs, and control robotic processes for enhanced efficiency and reduced downtime.
- Healthcare: From assisting with diagnostic support by analyzing medical images and patient data, to personalizing treatment plans and streamlining administrative tasks, AI agents revolutionize patient care and operational flow.
- Legal & Compliance: Agents can synthesize vast amounts of legal texts, identify relevant precedents, automate compliance reporting, and even assist in drafting legal documents, similar to First Line Software’s RegulationAI solution.
- Customer Service & Sales: AI-driven chatbots and voice assistants, increasingly behaving as true agents, can provide 24/7 support, personalize sales interactions, and manage complex customer inquiries, as seen in AI-Powered Sales Assistants and AI-Powered Customer Voice Assistants.
- Research & Development: Agents accelerate discovery by analyzing scientific literature, designing experiments, and simulating complex scenarios in fields ranging from pharmaceuticals to material science.
- Education: Personalized learning paths, intelligent tutoring systems, and automated grading can significantly enhance educational outcomes and teacher efficiency.
How to Manage AI Agents
AI Managed Services go beyond initial deployment, providing comprehensive support to ensure AI agents operate efficiently, securely, and effectively in the long term. These services typically include:
- Continuous Monitoring and Observability: Implementing sophisticated tools to constantly track agent performance, resource utilization, and key metrics. This involves logging every agent decision and interaction, creating detailed dashboards for observability, and setting up alerts for anomalies. This allows for proactive identification of issues like performance degradation, increased latency, or unexpected behavior.
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Integration: Designing workflows where human experts can intervene to validate agent decisions, correct errors, provide feedback, and handle complex edge cases that the agent cannot resolve autonomously. This ensures accuracy and maintains control.
- Performance Optimization and Retraining: Regularly analyzing agent performance data to identify areas for improvement. This includes fine-tuning LLM prompts, optimizing tool usage, and orchestrating periodic retraining of the agent’s underlying models with new data to prevent drift and maintain accuracy.
- Security and Audit: Implement robust security measures tailored for AI systems, including secure API access, data encryption, and access controls. Auditing capabilities are crucial. There is also a whole bunch of predictive AI-based analytics, providing a traceable record of agent actions and decisions for compliance, debugging, and accountability, especially in regulated industries.
- Scalability and Infrastructure Management: Managing the underlying infrastructure to ensure agents can scale seamlessly with demand. This includes provisioning compute resources, optimizing database performance, and ensuring high availability, often leveraging cloud platforms.
- Version Control and Rollback: Managing different versions of agent models and configurations, allowing for seamless updates and quick rollbacks in case of issues.
- Prompt Engineering and Maintenance: Continuously refining the prompts used to guide LLMs within the agent, adapting them to new requirements or to address emergent behaviors.
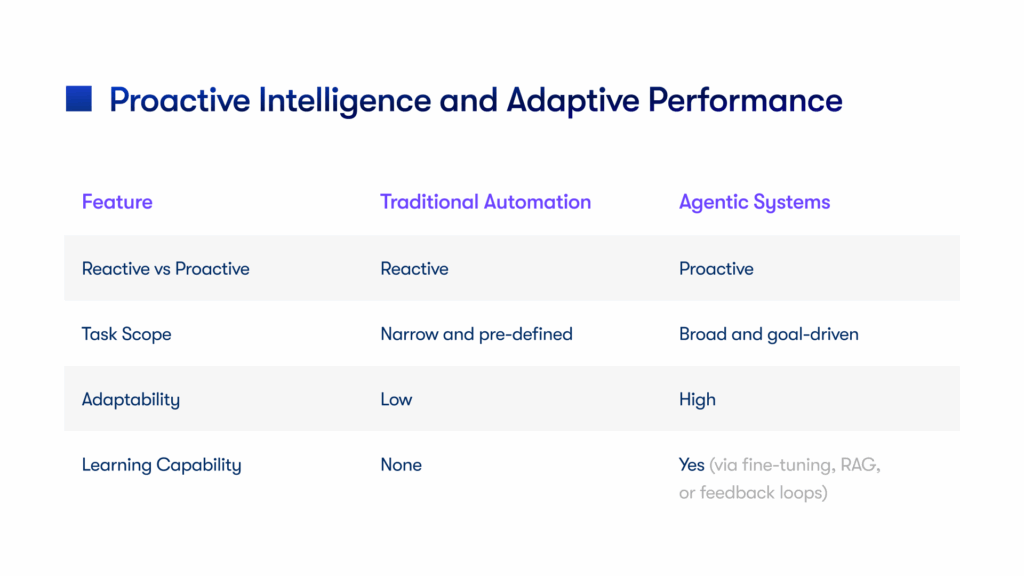
Firms like First Line Software, in addition to their development capabilities, explicitly offer AI Managed Services, acknowledging that successful AI implementation, particularly for agentic solutions, requires continuous integration, scaling, and operational management to truly drive business outcomes. This comprehensive approach, from consulting and proof-of-concept development to full implementation and ongoing management, is becoming the preferred model for organizations to harness the power of AI agents effectively and responsibly.
Navigating the Uncharted: Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the promise of AI agents is compelling, their broad implementation brings forth considerable challenges and ethical dilemmas that organizations must address directly.
- Data quality and bias: AI agents are only as effective as the data on which they are based. Biased, incomplete, or unstructured data can lead to ineffective agents that provide inaccurate outputs or perpetuate existing societal inequalities, particularly in sensitive areas like lending, hiring, or healthcare. Ensuring diverse, representative, and clean datasets is crucial.
- Algorithmic transparency and explainability: as AI agents increasingly make critical decisions, the “black box” problem becomes more pronounced. Understanding how an agent arrived at a specific decision is vital for accountability and trust. Regulations, such as the EU AI Act, are beginning to mandate transparency and human oversight, which may necessitate a reassessment of how agentic systems are designed and deployed.
- Amplified security vulnerabilities: memory poisoning, prompt injection, and privilege misuse represent new attack vectors that demand specialized defenses. As AI agents gain autonomy and access to sensitive systems, robust cybersecurity measures, including stringent access controls and continuous monitoring, become absolutely imperative. Firms offering AI Red Teaming services, like First Line Software, are emerging to help stress-test these systems against adversarial scenarios.
- Accountability and responsibility: When an autonomous AI agent makes a harmful decision, who bears the responsibility? Is it the developer, the deploying organization, or the AI itself? Establishing clear accountability frameworks and regulatory standards will be essential for fostering trust and ensuring responsible deployment.
The New Role of the Human Worker
As AI agents take on repetitive tasks, the human role evolves. We become conductors of powerful symphonies, no longer responsible for playing every single note. This shift creates a demand for uniquely human skills:
- Critical Thinking & Oversight: Humans are the “common-sense layer” that guides AI. We are responsible for validating the agent’s work, correcting its errors, and ensuring its outputs align with our values and goals. This human-in-the-loop model is not a temporary solution; it is the core of responsible and effective AI deployment.
- Creativity & Strategy: With the burden of repetitive work lifted, we are free to focus on what AI can’t do: innovate, strategize, and build. We can design new business models, develop breakthrough products, and create compelling customer experiences that are truly unique.
- Empathy & Communication: AI can process data and, as recent research has proven, be empathic, but it cannot connect with people contextually. Roles that require negotiation and relationship-building will become even more valuable. In a world of automated efficiency, human connection will be the ultimate competitive advantage.
The Collaborative Future: Humanity Amplified
- Start with purpose
- Deploy agents first, where they reduce drudgery (E.G., RegulationAI for compliance)
- Measure human impact
- Track “Amplification Metrics”: (Human Creativity Hours) × (Agent Efficiency Gains)
- Invest in symbiotic skills
- Reskill teams for AI Orchestration Using Programs Like:
- AI-driven educational programs
- American Federation of Teachers (AFT) AI Training Hub: Backed by $23 million from Microsoft, OpenAI, and Anthropic, the AFT is launching an AI training hub for educators, featuring workshops on using AI tools for lesson planning and student engagement.
- Virginia AI Certification Courses: In partnership with Google, Virginia is offering free and low-cost AI certification courses to up to 10,000 residents, aiming to equip job seekers with essential AI skills.
- American Federation of Teachers (AFT) AI Training Hub: Backed by $23 million from Microsoft, OpenAI, and Anthropic, the AFT is launching an AI training hub for educators, featuring workshops on using AI tools for lesson planning and student engagement.
- Design for joy
- Use agents to eliminate repetitive tasks—not replace human judgment.
The narrative of human obsolescence is a misconception. The rise of AI agents is not an ending but a new beginning—a chance to elevate our work, amplify our impact, and unlock a new era of human potential. The most successful organizations of the future will not be those that replace humans with machines, but those that master the art of combining them.
The Agent-Driven Future
Despite these tectonic shifts, the trajectory is clear. The global market for AI agents is projected to expand significantly, underscoring widespread confidence in their transformative capacity. The coming years will likely witness a surge in proactive, context-aware, and collaborative multi-agent systems. Ensembles of specialized agents will handle domain-specific tasks, and memory-augmented agents will provide increasingly personalized and nuanced interactions.
For businesses across all sectors, investing in AI agent technology is no longer an option but a strategic imperative. Firms that embrace this evolution, while meticulously addressing the inherent challenges and leveraging the support of managed AI services, stand to gain a substantial competitive edge in terms of efficiency, innovation, and responsiveness. The autonomous revolution of AI agents is underway, poised to fundamentally reshape the very structure of work, decision-making, and value creation in the digital age.
The future belongs not to AI or humans alone—but to teams that fuse human wisdom with agentic precision. Are you with us?
